Best viewed in Chrome
ED/ CONSULT NOTE
(Printable Forms: Trauma / Abscess)
DON'T Blindly Copy & Paste. READ/EDIT the Note!
OMFS Consult Note: _/_ / 2013, : AM / PM
NAME: ___,
MR#:___,
DOB: _/_ /_
CC/HPI: _ y/o (status (s/m/w/d) ____________) (race: ______) male / female presents to JMC / NCB ED with
PAIN: ___/10 (–) LOC: Duration: _, (–) Nausea: x _, (–) Vomiting: x_
PMH: Unremarkable / Asthma (last attack______, (–) hospitalized, (–) intubated) / DM (on/off insulin) / HTN / HLD / CHF
Meds/Vitamins/Herbals:
Allergies: NKDA
PH: never been hospitalized
PSHx:
FMHx:
SoHx:
- Smoking __ cigs/ppd x _ yrs,
- EtOH __ beers/drinks per day/week,
- Illicit drugs (marijuana, cocaine, PCP, etc.)
ROS:
Physical Examination
VS: BP: _/ _ ; PR: _ ; Tc: _ F; Tm: _ F; RR: _ ; O2 sat: ________ % on RA (2L NC)
GEN:
HEENT:
RESP:
CVS:
ABD:
EXT:
NEURO:
PSYCH:
LABS: 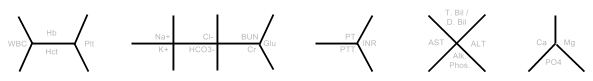
CBC: _ > _ / _ < _
BMP: ___/___, ___/___, ___/___ < ____
Radiographic Findings:
CT Head:
A/P: _____y/o male/female presents to ED with ......
Resident(s):
First & Last Name, DMD/DDS
OMFS PGY_
Attending:
First & Last Name, DMD
Consultation Request:
Reason for consultation: 30 y/o male presents for 1 wk f/u s/p ORIF of multiple mandible fractures. Pt. has PMH of…. Please evaluate & provide any recommendations including risk stratification, modification & recommendations for removal of teeth/archbars/ under IV sedation
COMPLETE History and Physical
(Printable)
Date: ___ / ___ / ___ @ ___: ___ am / pm
NAME:
MR#:
DOB:
Identification: Patient’s name, age, race, sex, occupation, marital status,
CC: In the patient’s own words, why he or she is there & how long the s/s were
HPI: Pt. states that he/she was assaulted by a friend 2hrs ago and was struck in the face with a bottle. She/he further states that the bottle shattered on the left side of her face cutting her left ear and resulting in pain in her left lower jaw. She is now unable to open or close her mouth fully. She denies LOC, headache, dizziness, light headedness or nausea/vomiting associated with the incident.
If (+) LOC, ask for duration, last remembered, 1st thing they noticed when the gain consciousness, and what was the pt doing at the time?
PMH:
- HTN
- DM2 (diet controlled / on insulin)
- HLD
- Asthma (last attack 2 months ago, hospitallized, intubated ..)
Past Hospitalizations: 2007, 2005 – childbirth
Preventive Health Maintenance (appropriate to age):
- Immunizations (Pneumo for >65):
- Last PPD/CXR:
- ECG:
- PAP test:
- Mammogram:
- Dental check-up:
- Vision:
- Hearing test:
MEDS:
- Albuterol inhaler prn
-
ALL: Penicillin–skin rash, Shrimp–Anaphylactic
PSHx: C–section x2 – 2007, 2005–no complications, Epidural anesthesia
- Transfusions: None
FMHx:
- Mother: 58–alive w/ HTN
- Father: deceased at age 50 due to gunshot wound.
- 3 Siblings alive and well.
- Health status or cause of death of parents, brothers or sisters, giving their current age or age at time of death. In addition to any known cause of death, give the chief symptoms of the illness. Note familial incidence of rheumatic disease, allergy, migraine, diabetes, hypertension, anemia, bleeding tendency, kidney disease, heart trouble, cancer, mental and nervous disorders, with special attention to the diseases suggested by the patient’s history.
SoHx:
- Birthplace:
- Unemployed / employed: school teacher
- Lives with: boyfriend & 2 children ages 2 and 4. No previous history of domestic violence,
- Tobacco: __ ppd x 10yrs = __ pack years
- EtOH: 5 x 40oz Colt 45s daily
- Illicit drugs: Cocaine (snorts 1/week), Marijuana
- Sexual Hx: orientation, partner(s), marriage, divorce, age and health of partner, children, satisfaction with sexual functioning, abuse, other problems e.g. erectile dysfunction, dyspareunia, libido.
REVIEW OF SYSTEMS:
GENERAL: Pt. generally in good health, obese, weight gain/loss, fatigue, recent illness, night sweats, fevers, weakness
SKIN: Rashes, hair/nail changes, pruritus, scaring, bruises, bleeding, texture/pigment changes
HEAD: Trauma, dizziness, syncope, headaches,
- EYES: Vision changes, glasses/contacts, photophobia, pain, conjunctivitis, diplopia
- EARS: Hearing, tinnitus, pain, vertigo, discharge,
- NOSE: Sinus problems, epistaxis, obstruction, changes, sinusitis
- OROPHARYNX: Bleeding gums, lesions, missing dentition
- THROAT: Swelling, goiter, thyromegaly, hoarseness
NECK: Pain, limitation of motion, swelling, masses, goiter
BREAST: Pain, masses, nipple discharge, lesions, plaque(s)
RESP: SOB (exertional, nocturnal, intermittent, constant), pleuritic pain, cough, productive cough, sputum, chest pains, pneumonia, hemoptysis,
CVS: chest pain, palpitations, orthopnea, dyspnea on exertion, murmurs, peripheral edema, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, edema, varicose veins, intermittent claudication
GI: appetite changes, dysphagia, abdominal pain, ulcers, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, hemorrhoids, blood in stools, jaundice, hernias, ascites
GU: dysuria, polyuria, nocturia, urinary frequency, incontinence, hematuria, UTI in the past, kidney problems,
REPRODUCTIVE:
- Males: urethral discharge, pain or masses in penis, pain or masses in scrotum or testicles, hernias
- Females: vaginal discharge, pruritis, lesions, pain, dyspareunia, dysmenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, menorrhagia, postmenopausal bleeding, odor
-> Menstrual history: Last Menstrual Period (LMP): ____________ or ____/_____/___
-> Age at menarche/menopause: _________
-> Obstetric history: Type of contraception used: _________, pregnancies: x _____, abortions: x ____, living children: x_____ , complications of pregnancy:_________________________________________
ENDOCRINE: weight loss, hot/cold intolerance, polydypsia, polyuria, polyphagia, goiter, excessive sweating, body hair changes
HEMOPOIETIC: bleeding tendency, easy bruisability, anemia, blood clots
MSK: pain, cramps, stiffness, fractures, dislocations, arthritis, limitations in movement, OA, RA
NEURO: dizziness, visual disturbances, paraesthesia, tremors, seizures, paralysis, gait disturbance, vertigo, memory defects, aphasia, dysarthria, incoordination, syncope.
PSYCH: depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, violent impulses, psychosis, suicidal ideations
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
GENERAL: well developed, well nourished, NAD, obsese, Alert & Oriented x 3 (to Person, Place, & Time), appropriately responsive. Pain of ___/10 in severity.
Height: ___' ____'' Weight: ___ lbs
V/S: BP: _____ / _____ Tc: _____ T Max: _____ Pulse: _____ Respiration: _____
SKIN: intact, lacerations, abrasions, contusions, swelling, rashes, tattoos, texture, color, moisture, eruptions, pigmentation, cyanosis, jaundice, petechiae, spider angiomata, distribution of hair
HEAD: normocephalic, atrumatic, lacerations, contusions, scalp tenderness
EYES: PERRLA (Pupils Equal Round Reactive to Light & Accommodation – focus on far/near objects), EOMI (Extraocular Movements Intact), sclera clear, gross vision intact, tearing, discharge, conjunctiva pink/red/bloody, glasses, periorbital ecchymosis, diplopia, blurriness
- Fundoscopic: discs normal, blood vessels normal, hemorrhages, exudates, pigmentation, lenticular opacities, retinal dislocation, papilledma
EARS: lacerations, discharge, hearing grossly intact, hemotympanum, Battle’s Sign/mastoid ecchymosis (Base of Skull/Middle Cranial Fx),
- Hearing: air conduction, bone conduction, tympanic membranes intact
NOSE: nares patent, symmetric, discharge, septal deviation, obstruction, epistaxis, crusted blood, congestion, septal hematoma, sinus tenderness
MOUTH & THROAT:
– EOE: swelling, pain, step defect, V3 parasthesia, Trismus (_____mm),
– IOE: uvula midline / deviated (R/ L), multiple missing teeth (pretrauma) #_________, malocclusion, swelling, lacerations, FOM bleeding, tongue papillary atrophy, tongue deviation, discoloration
NECK: thyromegaly, JVD, carotid pulsation, abnormal pulsation, tracheal tug, trachea midline, stiffness, range of motion intact
LYMPH NODES: LAD, tenderness of cervical, mandibular, supraclavicular, axillary, epitrochlear, inguinal glands
SPINE: Vertebral tenderness, curvatures, mobility intact, kiphosis, CVA tenderness
CHEST: Conformation, symmetry, mobility, abnormal pulsation, retro manubrial dullness, dilated veins
BREAST: Appear normal and symmetrical, tenderness, masses, discharge, plaques
RESP:
- Inspection: cough, type of respiration, symmetry of respiratory movements, adequacy of respiratory movements
- Palpation: fremitus
- Percussion: resonance, lung borders & their mobility.
- Auscultation: CTA B/L, equal breath sounds, wheezing (isp/ exp), crackles (coarse/fine), friction rubs, egophony
CVS: Normal S1 S2, RRR, S2 splitting , murmurs, friction rub, gallops, PMI shifted (L/ R), precordial heave
ABDOMEN: soft, non-tender, non-distended, BS present x 4 quadrants
RECTAL: Declined / Deferred / Not indicated
- Hemorrhoids, fissures, fistulae, sphincter tone intact, tenderness, masses, prostate, FOBT (+/-)
EXTREMITIES: FROM x 4 extremities w/ no limitations, UE strength (L: 5/5, R 4/5), LE strength (L: 5/5, R 4/5)peripheral pulse palpable, pulses equal (carotid, radial, femoral, popliteal, dorsalis pedis, posterior tibial pulses), varicosities, clubbing (fingers / toes), LE edema
NEURO: CN II–XII appear grossly intact, AO x3, appropriately responsive, follows commands, gait disturbance, dysdiadochokinesia, finger-to-nose intact
- Reflexes:
-> Normal: patellar, biceps, ankle, abdominals.
-> Abnormal: Babinski, Hoffman, clonus
GENITALIA: Declined / Deferred / Not indicated
- Male: urethral discharge, lesions on penis, hydrocele, varicocele, testicular masses, hernias
- Female:
-> Pelvic examination: vulvar lesions, vaginal discharge
-> Cervix: inflammation, friability, discharge
-> Uterus: position, enlarged, tenderness
-> Adnexae: masses, tenderness
LABS: 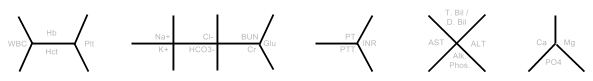
- CBC: _ > _ / _ < _
- BMP: ___/___, ___/___, ___/___ < ____
EKG: NSR @ 75 bpm, no ST or T wave changes
RADIOGRAPHS:
- CT Head:
- CT Chest:
- CXR:
- MIR:
ASSESSMENT: ___ y/o m/f
Case discussed with Chief Resident/Attending – Pt. to be admitted.
PLAN:
- Admit to OMS Service Dr. ....
- IV antibiotics – Clindamycin 300mg IVPB q6h
- Pain manangement – Motrin elixir 600mg PO q6h prn pain
- Dressing change by nursing q6h
- Obtain Panorex – transport to dental clinic – AM
- DVT PPX: SQH / Lovenox
- Diet: Full liquid / Diabetic / Cardiac / Low K+ / Low Na+
Dispo: Pt. to be d/c after surgery to repair Left mandibular angle fracture. Estimated stay of 4 days.
First Name, Last Name DMD/DDS
OMFS Resident
First Name, Last Name DMD / DDS, MD
Attending
Standard Admission Doctor's Orders
Date: ___ / ___ / 2011 Time: ___ : ___ am / pm
Admit to OMFS Dr. _______________
Dx: Left/Right Mandible Fracture, R/L ZMC Fracture
Condition: Stable
Vitals: Every Shift
All: NKDA
Activity: OOB (Out Of Bed)
Nursing: Suction at bedside, Head of bed elevated 30 degrees, Ice pack to face
Diet: Clear Liquid / Puree / Soft / Regular
IVF: D5 0.45% NS 1,000ml @ 50/100mL/hr
Meds:
- Motrin (600mg) po q6h pain,
- Morphine Sulfate (4mg) SC q4h prn process if severe pain
- Percocet (3mg/325mg) prn/q4h process if moderate pain
- Benadryl (50mg) prn at bedtime
- Zofran (4mg) IV/IM prn (anti-nausea)
- Famotidine (20mg) po bid (only if the pt. is NPO overnight)
- Decadron (8mg) IVSS q8h
Antibiotics:
- Unasyn (Ampicillin + Sulbactam) (3g) IVSS q6h between 15 & 30 minutes
- Clindamycin (600-900mg) IV q6h
Labs:
- CBC,
- SMA7 (Basic Metabolic Panel),
- UA,
- PT/PTT, INR,
- Type & Screen (Blood type)
CMP (Comprehensive Metabolic Panel - includes LFTs)
Other:
- EKG (>50 y/o),
- Chest x-ray (>50 y/o), β-HCG
Please have patient transported to Dental Clinic tomorrow @ 8am for Panorex - Please arrange transportation as necessary
Standard AM Note
Oral Maxillofacial Surgery Progress Note
Pt:
MRN #:
DOB:
S:
Pt. examined at bedside. No events overnight. Pt. is in mild pain but controlled with medication. Pt. denies any nausea, vomiting, fevers, chills, shortness of breath, chest pain, abdominal pain. Pt. feels like he is improving.
O:
Vitals: BP: _ / _ P: _ R: _ T: _ O2: _ % RA
GEN: NAD, Pt. is lying upright comfortably in bed, breathing comfortably on RA
H: NC/AT, no scalp tenderness
E: EOMI, PERRL, gross vision intact
E:Gross hearing intact, TMs clear b/l
N:Nares patent, MMM, no septal deviation
T: uvula midline,
IOE: MIO: _ mm, FOM,
Neck: supple, thyroid midline, no LAD
PULM: CTA B/L
CVS: RRR, S1/S2
ABD: NT/ND, soft, + BS
EXT: FROM x4, not limitations, WWP, distal pulses equal b/l
Neuro: AAOx3, CNII-XII grossly intact, no focal deficits
Labs:
CBC: > / <
Chem: / , / , / <
A/P: __ yo
- c/w Abx (Unasyn 3g q6h)
- c/w __ diet
- OR on __
- NPO after midnight
- HOB elevated, yankauer at bedside
- Care as per primary team
- Please call or page OMFS with any questions
OMFS Pre-Op Note
Pre-Op Diagnosis: Left ZMC Fx
Planned Procedure: ORIF Left ZMC Fx
Labs:
- CBC: _ > _ / _ < _
- BMP: ___/___, ___/___, ___/___ < ____
- PT/PTT: 10.6,/ 24.6, INR: 1.1
- Type & Screen: B Positive
CXR: WNL – no abnormalities or pathology noted. A – airway intact, B – no fractures noted/no pleural effusion or infiltrate, C – cardiomediastinal silhouette is not enlarged
EKG: None
Orders:
- VS Qshift
- D5 ½ NS at 130 cc/hr (@ 0.5ml/kg/hr)
- HOB elevated 30 degrees
- OOB TID
- Clindamycin 900mg QH8
- Pseudoephedrine 30 mg Q6H Prn
- Morphine 4mgQ4H prn pain
- Ibuprofen 400mg Q6H prn pain
- Percocet 1-2 tabs Q4H prn pain
- Zofran 4mg Q8H prn nausea
- Benadryl 50mg Prn QD
- Heparin 5000 units SQ Q8H
- SCDs
- regular diet qmeal
Consent: Signed, in medical record. Risks and benefits explained. Discussed complications, including, but not limited to, pain, swellin, bleeding, infection, need for further surgery, malunion, nonunion, damage to adjacent structures, damage to nerves, noncosmetic result, and death. Questions answered.
First Name Last Name, DMD
OMFS Intern/Resident
OMFS Post-Op Note
Admit to: PACU for 23 hour admission, then 3A/4A
Diagnosis: Left ZMC Fx
Condition: Stable
VS: q2h, the per routine
ALL: NKDA
Activity: Up with assistance until stable, then ad libitum
Diet: Clear liquids, advance to full liquid as tolerated
Orders:
- HOB at 30 degrees
- Yankauer suction at bedside
- Foley to gravity
- No pressure to face or chin
- Wire cutters at bedside
- Strict I&Os
- IVF: D5 and 1/2 NS at 100ml/hr
- Pain meds: Ibuprofen 400mg q6h prn pain, Percocet 1-2 tabs q4h prn mod-severe pain, Morphine 4mg q4h prn severe pain,
- ABx: Clindamycin 900mg QH8
- Decadron 8mg q8h 3 times, first dose 4h after last OR dose
First Name Last Name, DMD
OMFS Intern/Resident
OMFS Discharge Summary
Name:
MR#:
Date of Admission:
Date of Discharge:
Admission Diagnosis:
Discharge Diagnosis:
CC/HPI:
ED Course:
OR Course:
Hospital Course:
Physical exam on discharge:
VS: T: , BP: , PR: , RR: , O2:
GEN:
HEENT:
CV:
PULM:
ABD:
EXT:
Neuro:
Discharge Assessment: Pt. stable for discharge home with/without services.
Discharge Plan:
Discharge patient to home.
Diet: Soft foods for 1 week, advance as tolerated
Activity: No heavy lifting for __ weeks.
Medications:
-
Instructions:
Followup: F/u with OMFS clinic (JMC 3rd Floor Bldg 1) in 1 week on _ / _ /13 at 8 am for __.
Consents (R/B/A, not limited to:)
Extractions:
Risks: pain, bleeding, swelling, infection, damage to adjacent teeth/structures, temporary/permanent numbness of the tongue/lips/chin/cheek, oro-antral communication
Benefits: relieft of pain, infection, removal of decayed tooth
Alternatives: none, RTC,
Risk of no Tx: pain, swelling, infection
ORIF:
Risks: pain, bleeding, swelling, infection, damage to adjacent teeth/structures, temporary/permanent numbness of the tongue/lips/chin/cheek, oro-antral communication, malocclusion, malunion, nonunion, scarring, need for secondary procedures, extraction of any necessary teeth, possible weakness of marginal mandibular branch of CN VII, damage to nerves, noncosmetic result
Benefits: reduction of fracture, relief of pain, restoration of occlusion
Alternatives: no tx
Risk of no Tx: pain, bleeding, swelling, infection, malocclusion
Blood Transfusions: (requires Type & Screen)
Risks:
Allergic reaction & hives, fever, actue hemolytic reaction, lung injury, blood-borne infectionm delayed hemolytic reaction, iorn overload, graft-vs-host disease
Benefits: tx for anemia, tx for blood loss, decrease anemic symptoms
Alternatives: no transfusion
Risk of no Tx: anemia, weakness, fatigue, dizziness
HEENT Physical Exams/Findings
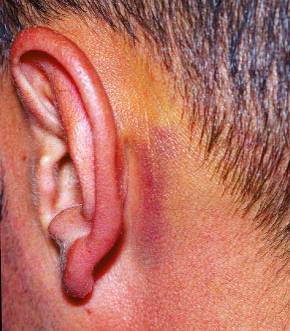
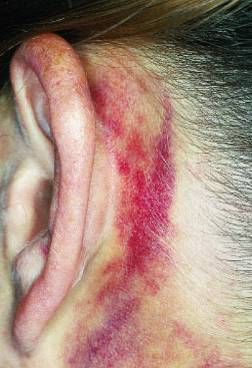
| Battle sign - Think Basilar Skull Fracture | ||||
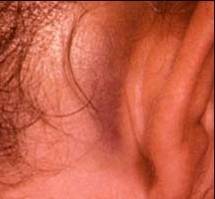 |
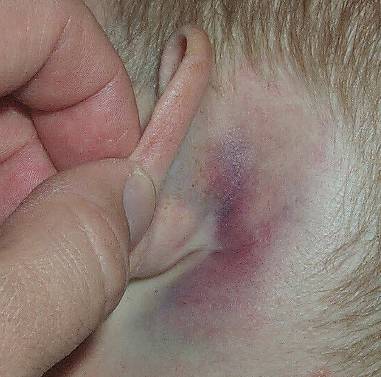 |
 |
 |
|
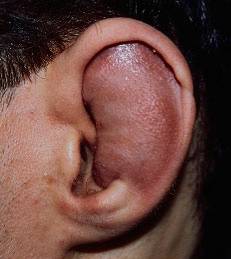
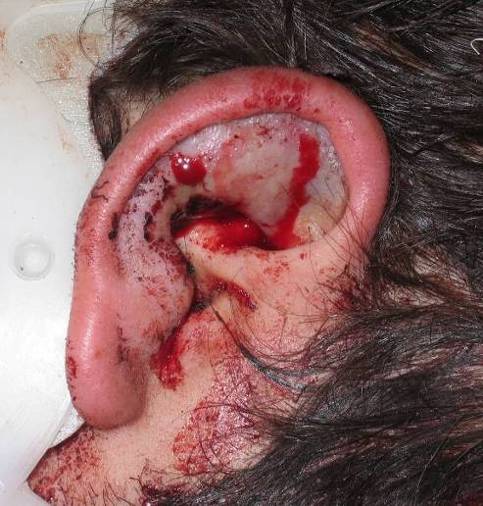
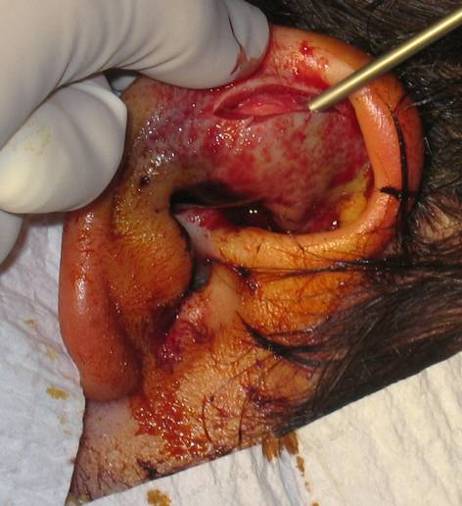
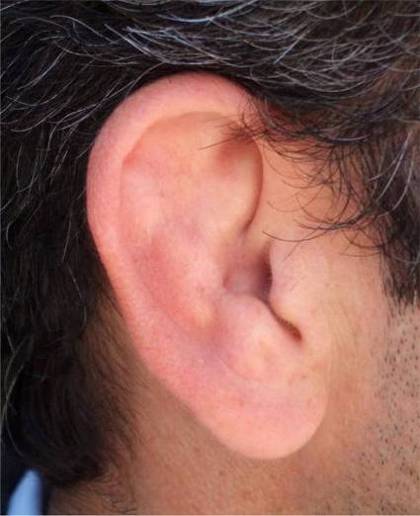
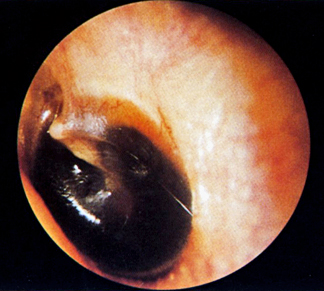
| Auricular hematoma may lead to Cauliflower ear | ||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
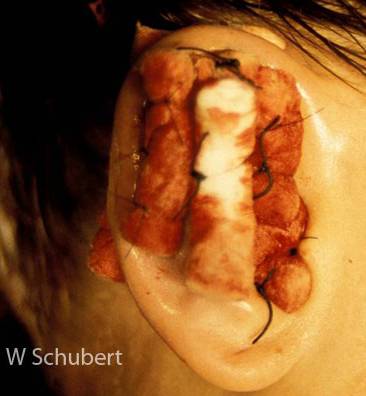
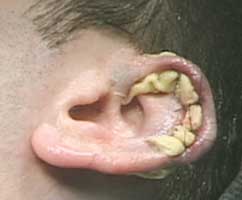
| Bolster dressing - Suture guaze tightly with silk sutures | ||||
  |
||||
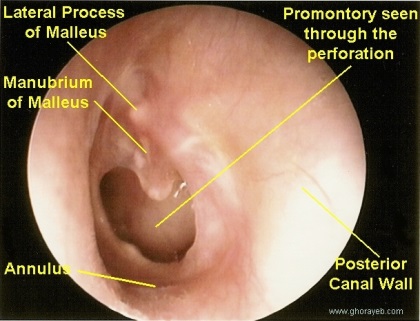
| Normal Tympanic Membranes | ||||
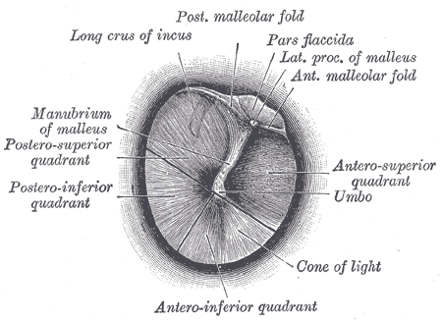
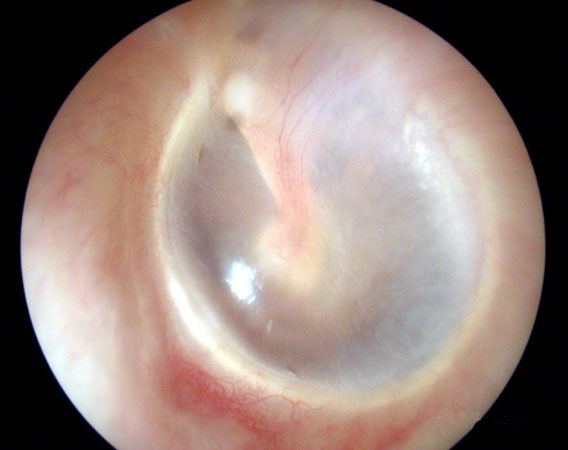
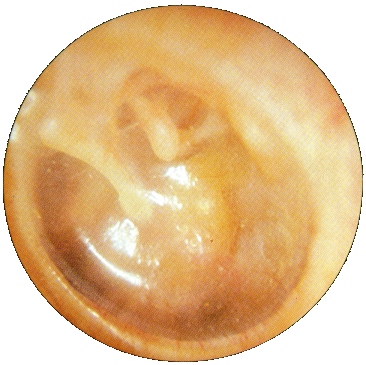 |
||||
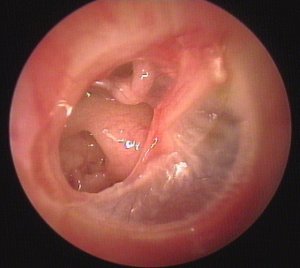
Abnormal tympanic membranes |
||||
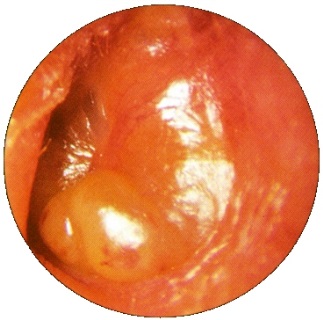 |
 |
 |
 |
|
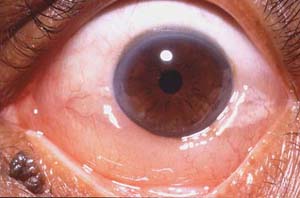
Chemosis: Swelling of the conjunctiva |
 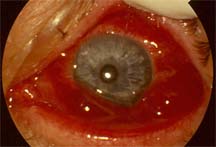 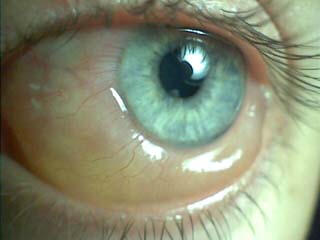 |
Ptosis: |
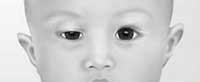 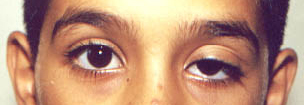 |
Hypertelorism: Increased inter-pupillary distance |
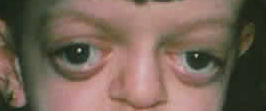 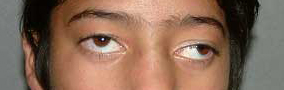 |
Telacanthus: Increased distance between the medial canthi of the eyes, while the inter-pupillary distance is normal (28 – 35mm) |
 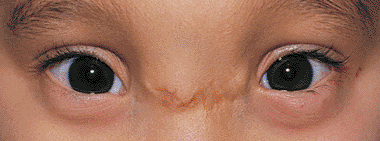 |
Retrobulbal Hemotoma: Increased bleeding behind the globe can lead to blindness |
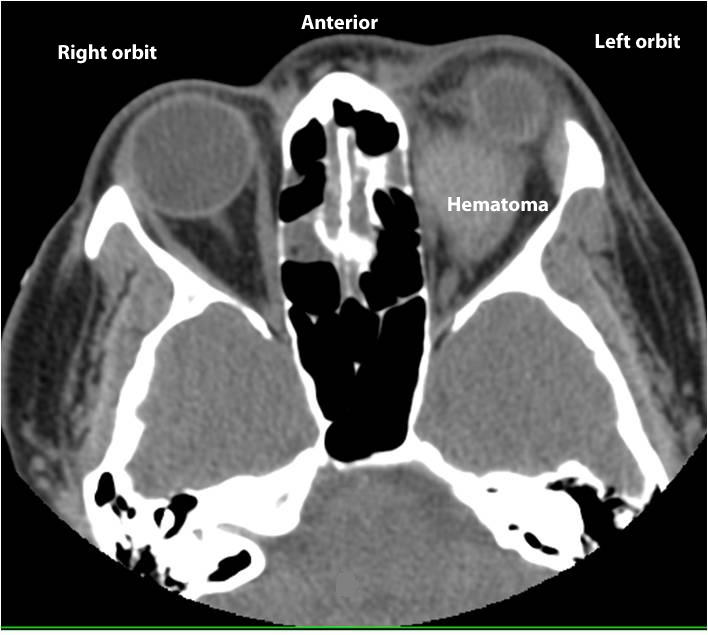 |
Oculocardiac Reflex (Aschner phenomenon, Aschner reflex, or Aschner-Dagnini reflex)
- Normal Intraocular Pressure is (10 - 20 mmHg)
- Bradycardia w/ traction applied to EOM and/or compression of the eyeball
- Mediated by CN III & CN X of parasympathetic sys
- Afferent: V1 synapses w/ visceral motor nucleus of CN X in the reticular formation of the brain stem
- Efferent: CN X from cardiovascular center in the medulla to the heart, of which increases stimulation, leading to decreased output of the SA node
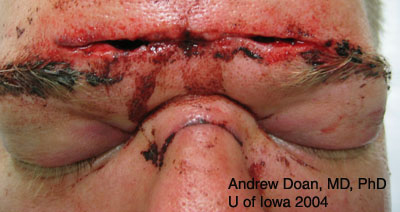
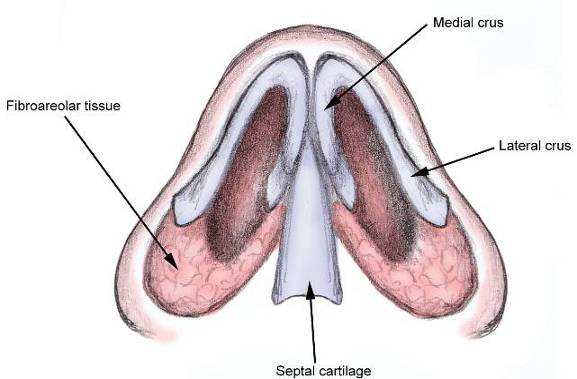
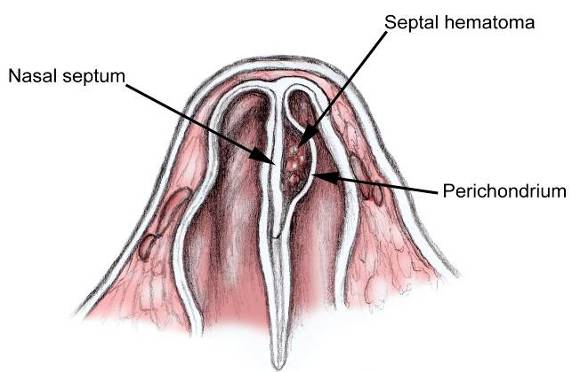
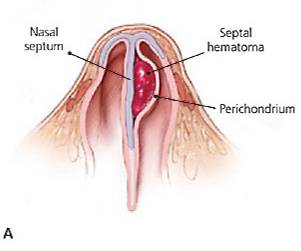
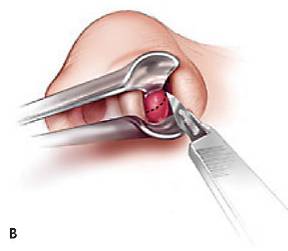
| Septal Hematoma | |||
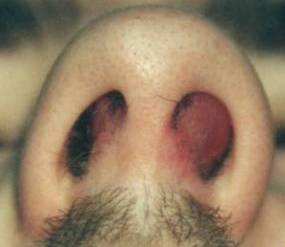 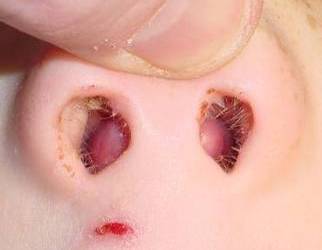 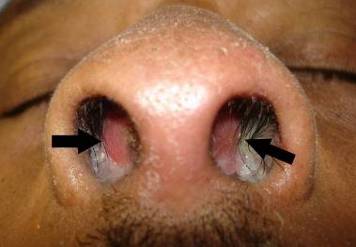 |
|||
| Treatment | |||
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
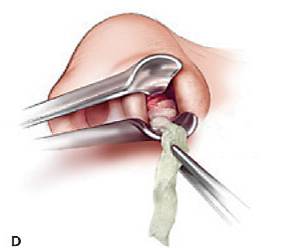 |
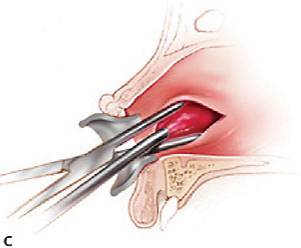
Procedures
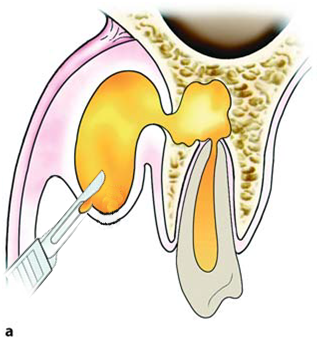
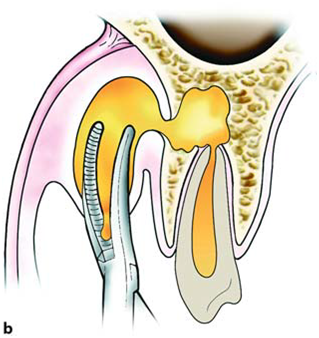
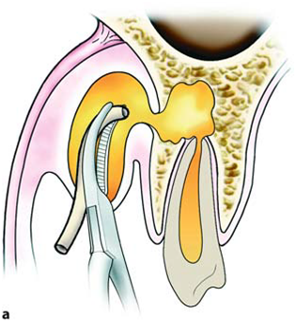
| Incision & Drainage | |
1) Contact bone at a 45 degree angle |
2) Insert hemostat CLOSED, dissect open, remove opened |
3) Insert drain w/ tissue pick-ups/hemostat (You can place a suture thru the drain prior to placement) |
4) Place 1-2 silk sutures to secure the drain |
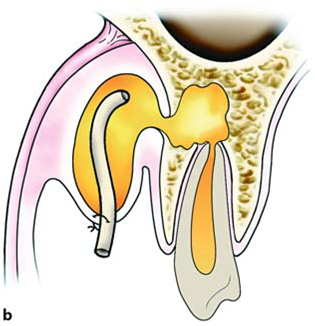
Sublingual abscess |
Palatal abscess |
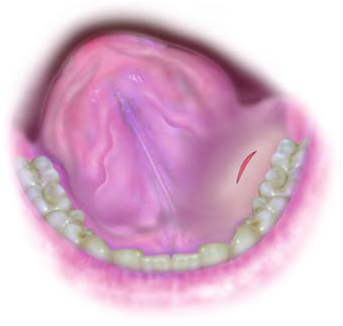
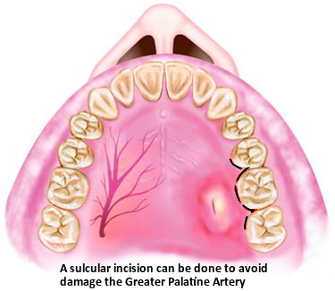
| External Approaches for I&D | |
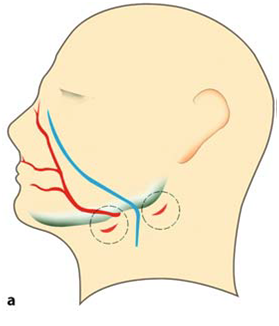 |
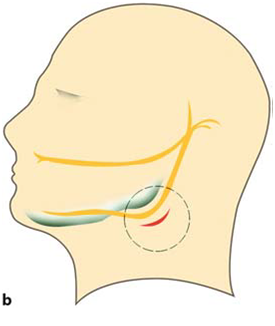 |
Suggested Sutures to Use
Copious irrigate & careful inspect the wound for foreign debris prior to placing sutures
Limit/Avoid the amount of epi in ears or nose due to cartilage
Cartilage has no blood supply and use of epinephrine can result in necrosis of tissue
Blue Prolene is advised around areas with black hair or dark skinned individuals
Midface Fractures
Fracture Type |
Prevalence |
|
Zygomaticomaxillary complex (tripod fracture) |
40 % |
|
LeFort |
I |
15 % |
II |
10 % |
|
III |
10 % |
|
Zygomatic arch |
10 % |
|
Alveolar process of maxilla |
5 % |
|
Smash fractures |
5 % |
|
Other |
5 % |
|
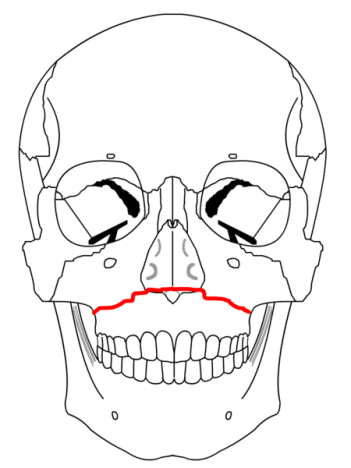
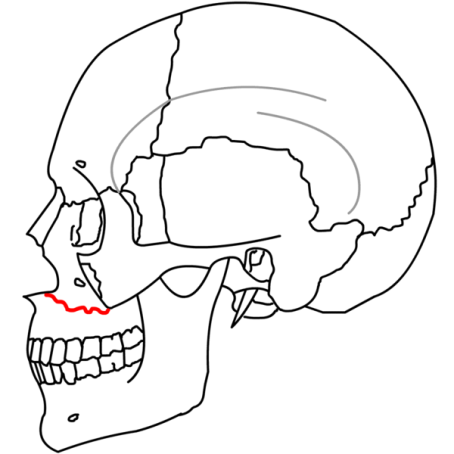
| Lefort I - Maxilla completely separately from the face - fracture goes thru the lateral pyriform rim, thru maxillary sinus wall, through tuberosity, and thru the pterygoid plates | |
 |
 |
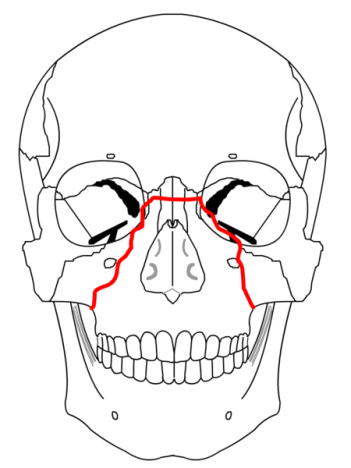
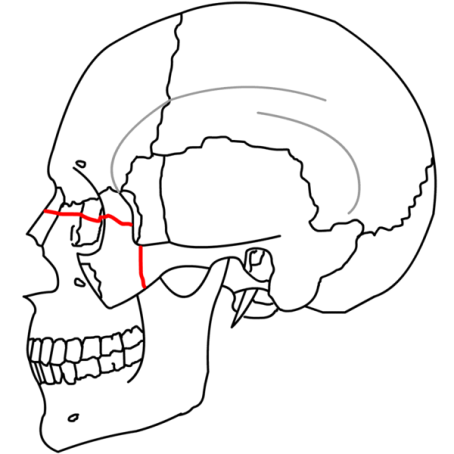
| Lefort II - Pyramidal shaped fracture - the fracture goes thru the nasofrontal suture, thru the lacrimal bones and down thru the infraorbital rims | |
 |
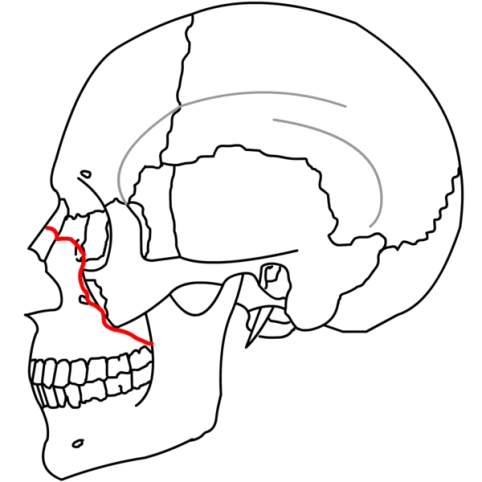 |
| Lefort III - Fracture course thru the nasofrontal suture, across the lacrimal bones, thru the inferior orbital fissure, across the lateral orbital rims and thru the frontozygomatic & zygomaticotemporal sutures | |
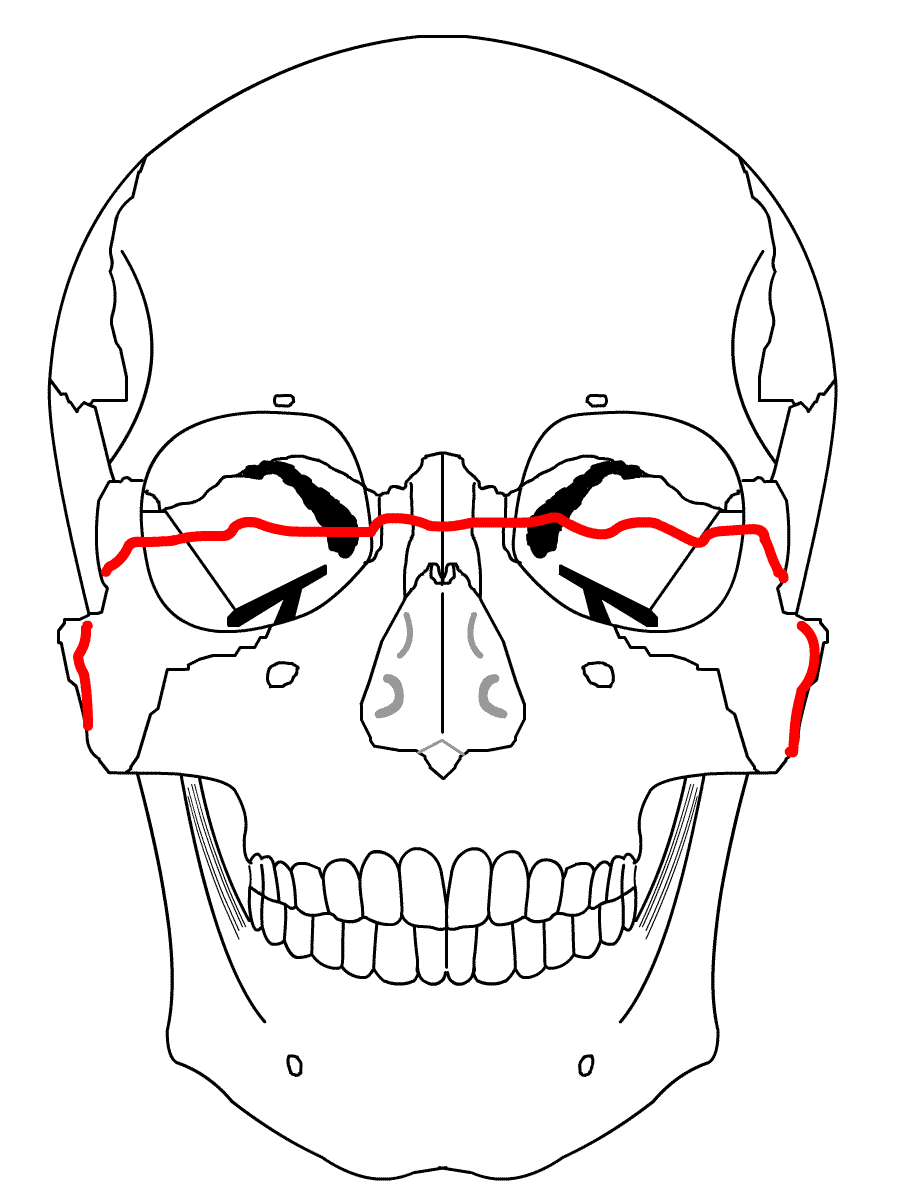 |
 |
Mandible Fxs
| 1) Angle - Located distal to the 3rd Molar 2) Body - Usually extends from the region of the distal canine to 2nd / 3rd molar region 3) Parasymphysis - Involves fx anterior to the canines 4) Midline/Symphysis - fx located between the central incisors 5) Ramus - fx located superior to the angle 6) Condylar - Involves the condylar process superior to the ramus 7) Subcondylar - fx below/involving the sigmoid notch 8) Coronoid - Located in the area of the coronoid process superior to the ramus |
Orbital Floor Fx
Orbital (~40 mm from infraorbital rim to optic foramen, 30cc volume)
Floor only (Blowout/Trapdoor fracture)
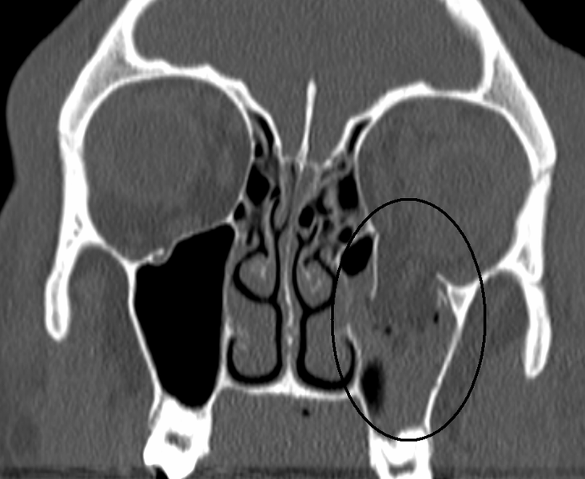
ZMC Fx
ZMC (Zymgomatico-Maxillary-Complex Fracture)
Floor only (Blowout/Trapdoor fracture)
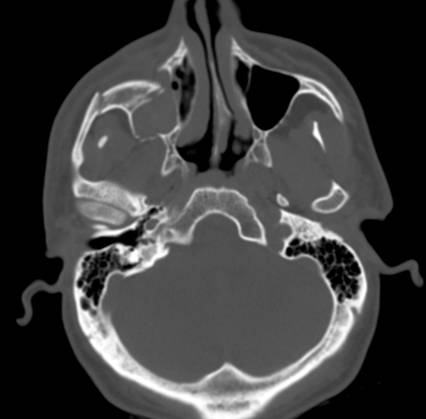
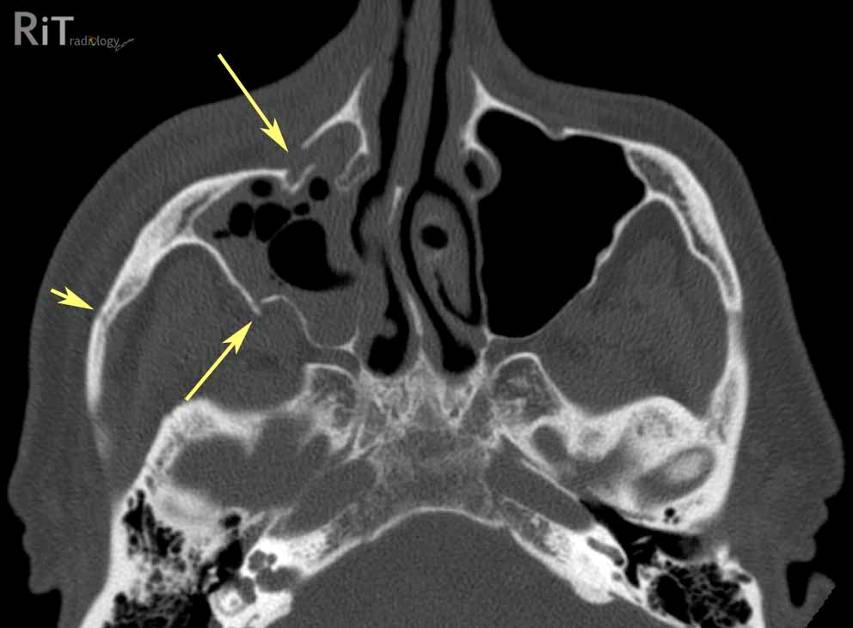
Zygomatic Arch Fx
coming soon...
Nasal Bone Fx
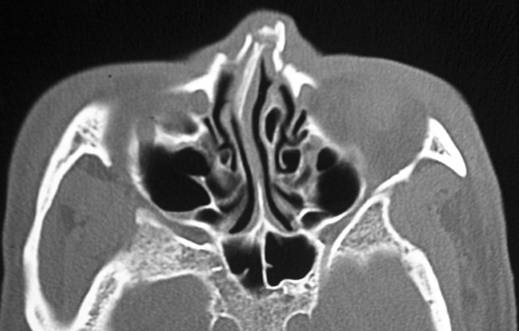
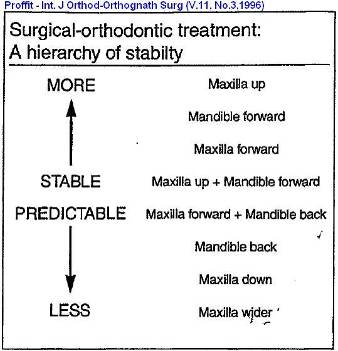
Orthognathics
Bite Wounds
Dog bites:
- Capnocytophaga ochracea (Gram-Negative) or Pasteurella multocida (Gram-Negative coccobacillus)
- Tx: Augmentin / Unasyn (3G IV)
- Check Tetanus & Rabies
Human bites:
- Eikenella corrodens (fastidious Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacillus)
- Tx: Augemtin / Unasyn
EtOH Withdrawal Tx
Alcoholic Seizures occur w/in 24hrs
DT can occur w/in 48-72hrs
Delirium Tremens (DT) Prophylaxis Regimen
Muti-vitamins
Thiamine 100mg PO / IM/IV daily
Folate: 1mg/day PO
Magnesium: the goal mg should be >2.0mg/dl
Benzodiazepine:
Generic Name Product |
1st Dose |
Time |
Duration |
2nd Dose |
Duration |
Chlodiazeposide (Librium) |
50mg |
Q6h |
24hrs |
25mg |
48hrs |
Diazepam (Valium) |
10mg |
Q6h |
24hrs |
5mg |
48hrs |
Lorazepam (Ativan) |
2mg |
Q6h |
24hrs |
1mg |
48hrs |
Multi-Vitamin, Folate, Thiamine |
|
|
|
|
|
Pt. w/ DT should be transferred to the ICU & managed medically
Signs & Symptoms of Alcohol Withdrawal
Tremor, restlessness, insomnia, nightmares, paroxysmal sweats, tachycardia, fever, nausea, vomiting, seizures, hallucinations (auditory, visual, tactile), increased agitation, & tremulousness
IV Fluids
| Fluid | Osmolality (mOsm/L) | Na (mmol/L) | Cl (mmol/L) | K (mmol/L) | Ca (mmol/L) | Mg (mmol/L) | Glucose (g/L) | Glucose (mmol/L) | Lactate (mmol/L) | Acetate (mEq/L) | Gluconate (mEq/L) | Notes |
| Blood (in vivo) | 278-305 | 135-145 | 95-108 | 3.5-5 | 1.1-1.4 | 0.75-1.2 | 0.65-1.1 | 3.6-6.1 | 1-1.8 | |||
| Normal Saline; 0.9% Saline | 308 | 154 | 154 | Isotonic | ||||||||
| Hartmann's; CSL (compound sodium lactate) | 281 | 131 | 112 | 5 | 4 | 29 | ||||||
| Hartmann's + D5W | 605 | 131 | 111 | 5 | 4 | 50 | 278 | Isotonic | ||||
| Lactated Ringer's | 275 | 130 | 109 | 4 | 1.5 | 28 | ||||||
| Plasmalyte | 294 | 140 | 98 | 5 | 1.5 | 27 | 23 | |||||
| 3% Saline | 1026 | 513 | 513 | |||||||||
| 5% Saline | 1710 | 855 | 855 | |||||||||
| Half Normal Saline; 0.45% Saline | 154 | 77 | 77 | Hypotonic | ||||||||
| Half Normal Saline + 5% Dextrose; 0.45% Saline + D5 | 432 | 77 | 77 | 50 | 278 | |||||||
| Bart's; D4S; 0.18% sailine + 4% Dextrose | 284 | 31 | 31 | 40 | 222 | |||||||
| 5% Dextrose; D5W | 278 | 50 | 278 | Isotonic |
Blood products
Type & Screen: Pt's blood type (ABO & Rh) screend for common antibodies
Cross-match: Pt's serum checked for preformed Abs vs the donor's RBCs
PRBCs:
- 1 unit = ~250 ml (should increase Hb by 1g/dL and increase Hct by 3%) transfused 3-4h/unit
Fascial Planes
Sagittal Section Showing Deep Cervical Fascial Layers
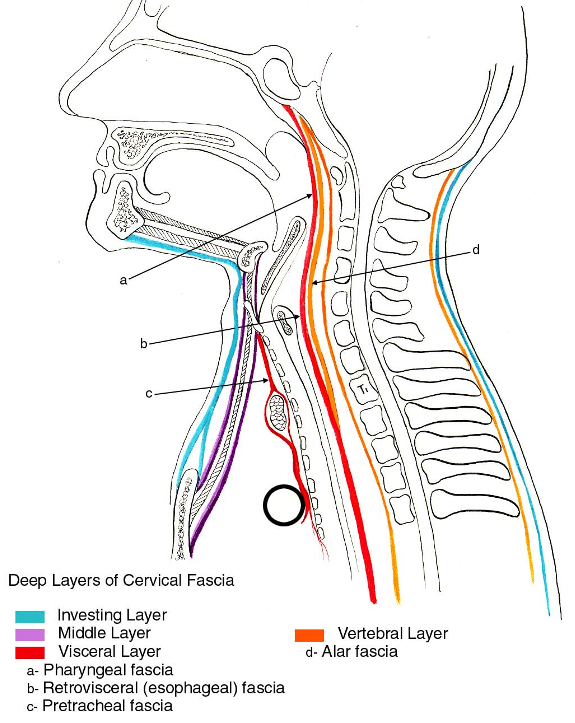
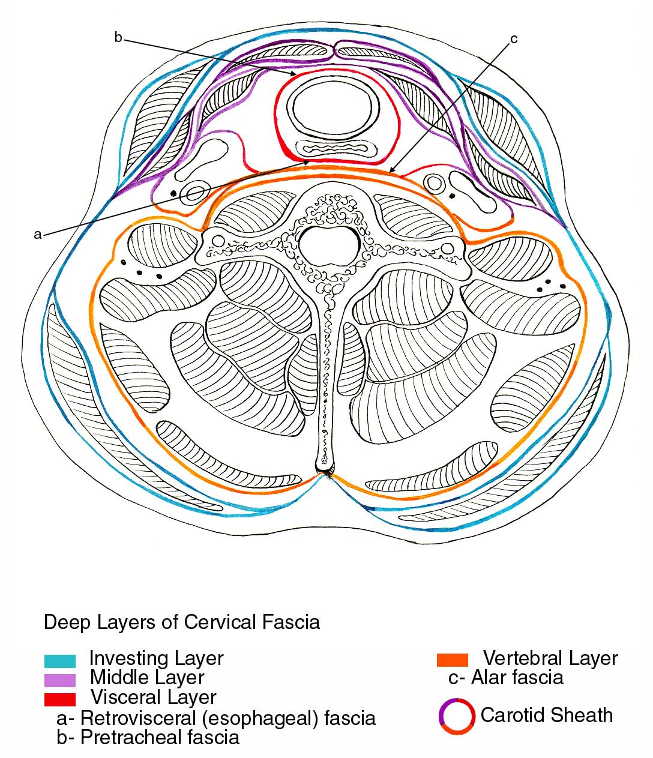
Infrahyoid Cross-Section Showing Layers of Deep Cervical Fascia
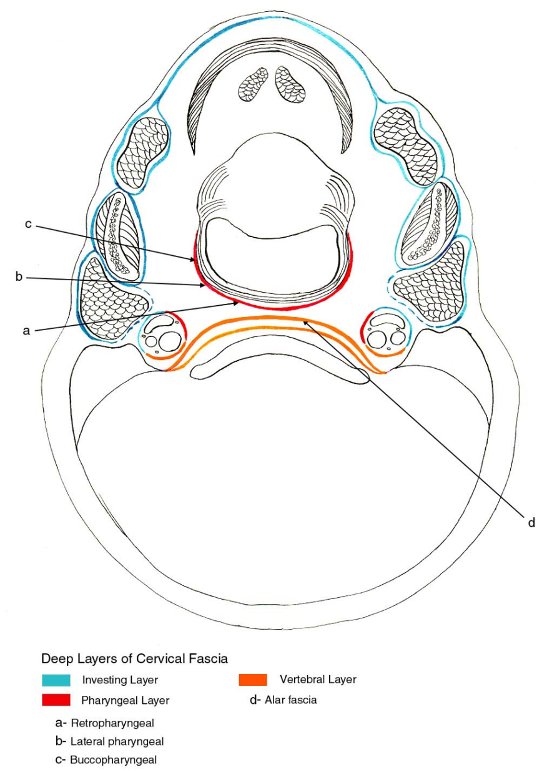
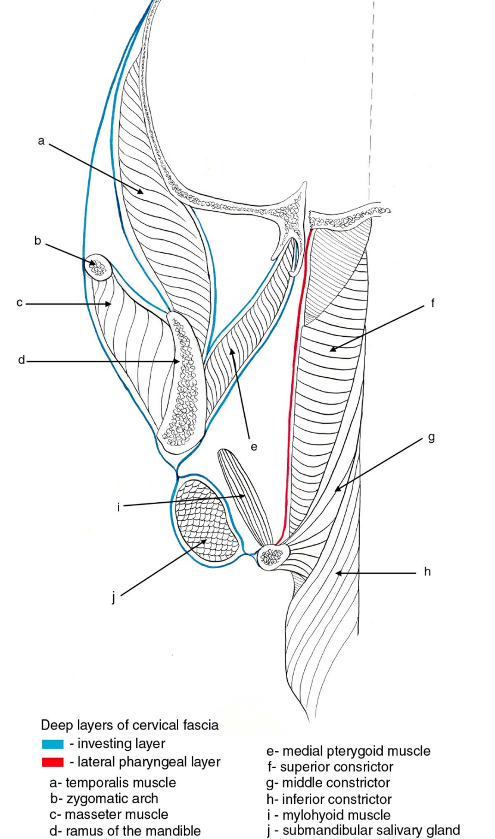
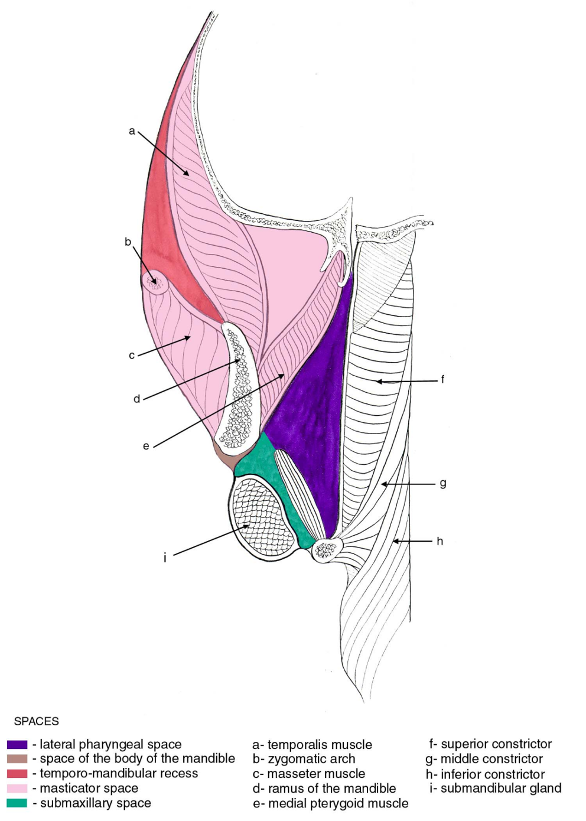
Suprahyoid Cross-Section Showing Layers of Deep Cervical Fascia
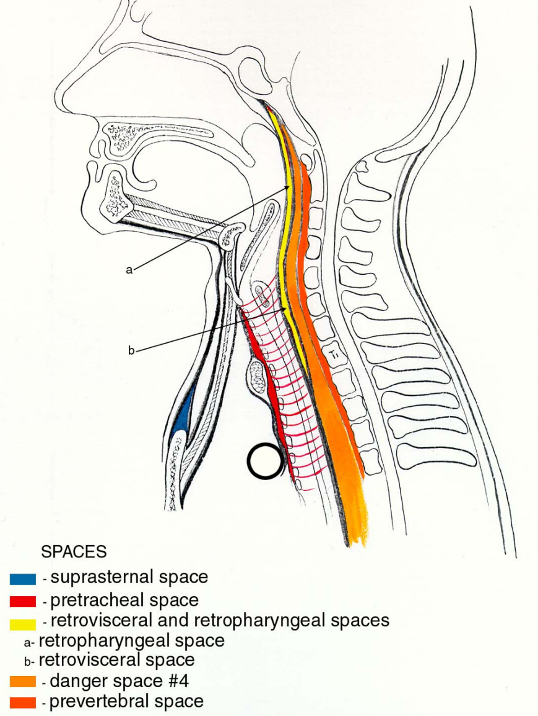
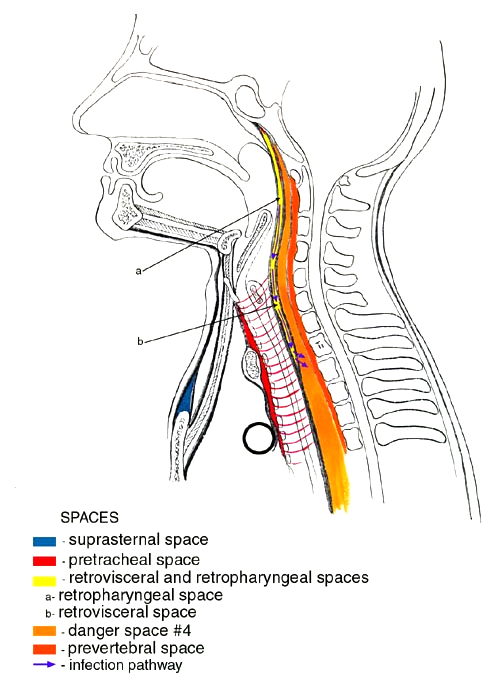
Sagittal Section Showing Fascial Spaces
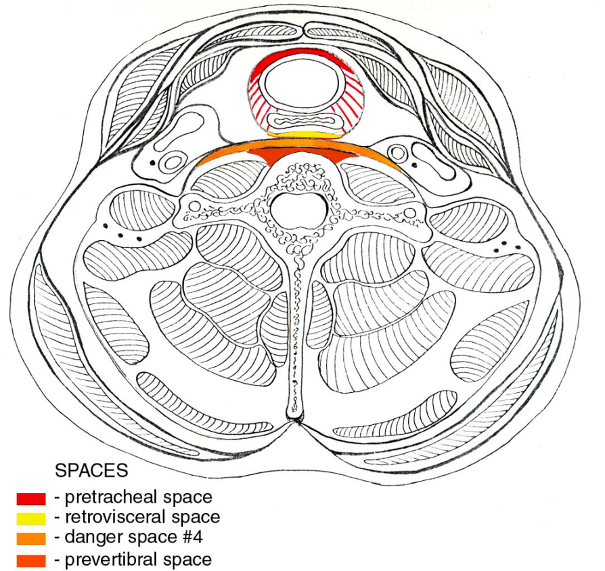
Infrahyoid Cross-Section Showing Fascial Spaces
Coronal Section Showing Deep Cervical Fascial Layer
Coronal Section Showing Fascial Spaces
Sagittal Section Showing Pathway of Infection
Suprahyoid Cross-Section Showing Pathway of Infection
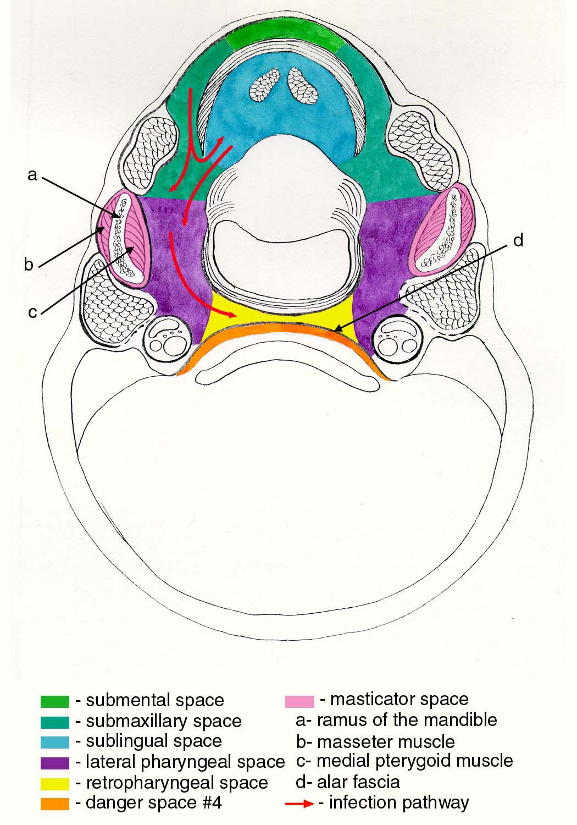
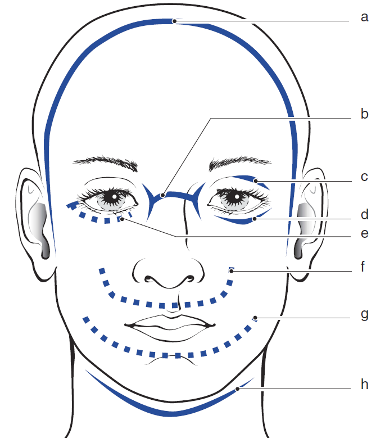
Surgical Approaches to the Face
| a | Bicoronal flap procedure: frontal sinus, naso-orbitoethmoid (superior aspect), medial canthal tendon, supraorbital rim, orbital roof, superior aspect of the medial and lateral orbital wall, zygomatic arch, and mandibular condyle (with preauricular extension) |
(Peterson's 2nd ed.) |
| b | Perinasal incisions: naso-orbitoethmoid region, medial canthal tendon, and nasolacrimal sac. These incisions are generally avoided because of the potential for significant scarring. This incision is not needed when the bicoronal incision is used.
Subciliary and transconjunctival incision with lateral canthotomy: infraorbital rim, medial and lateral orbital wall, and orbital floor |
|
| c | Upper eyelid crease incision/Superior Tarsal crease: superior and lateral regions of the orbit. It is generally used to expose the frontozygomatic suture. This incision is not needed when the bicoronal incision is used | |
| d | Subciliary: infraorbital rim, medial and lateral orbital wall, and orbital floor | |
| e | Transconjunctival incision with lateral canthotomy does allow access to the frontozygomatic suture. This requires detachment of the lateral canthal tendon and incision through the orbicularis oculi muscle and periosteum deep to the lateral periorbital skin. The subciliary approach may allow better access to the lateral nasal region | |
| f | Maxillary vestibular incision: maxilla and zygomaticomaxillary buttress | |
| g | Mandibular vestibular incision: mandible from the ramus to the symphysis. This approach is not usually recommended for comminuted fractures – Skip Premolar area | |
| h | Cervical incisions: mandible, except for when there is a high condylar neck fracture. The approach is generally indicated when anatomic reduction is crucial. It allows the surgeon to visualize the reduction of the lingual cortex. It is also indicated for comminuted and complicated fractures such as a fracture of the atrophic edentulous mandible |
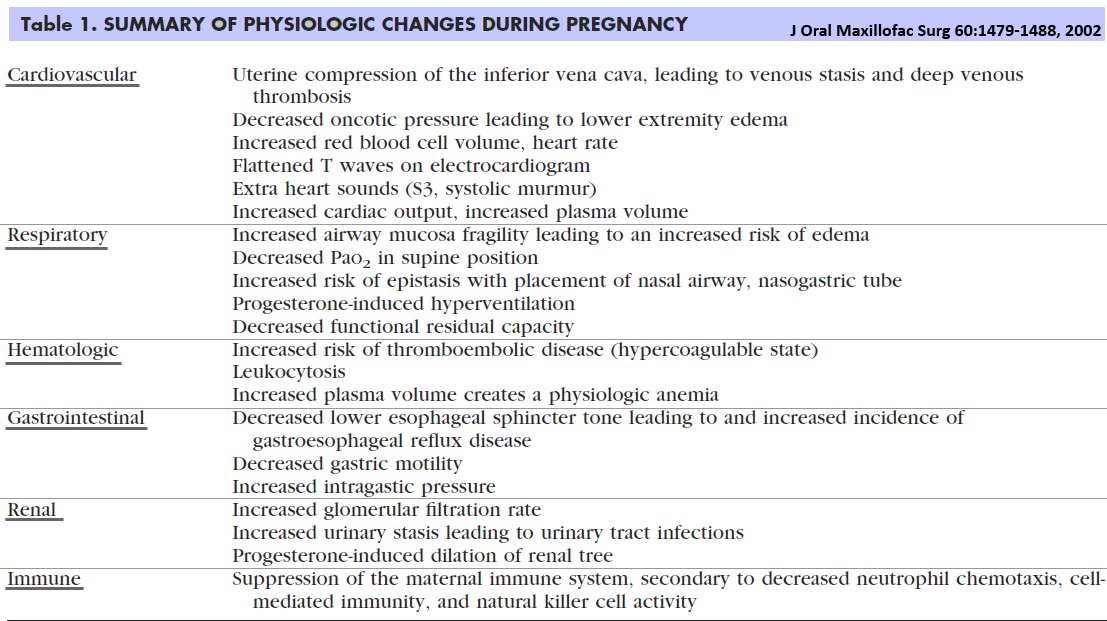
Physiologic Changes During Pregnancy
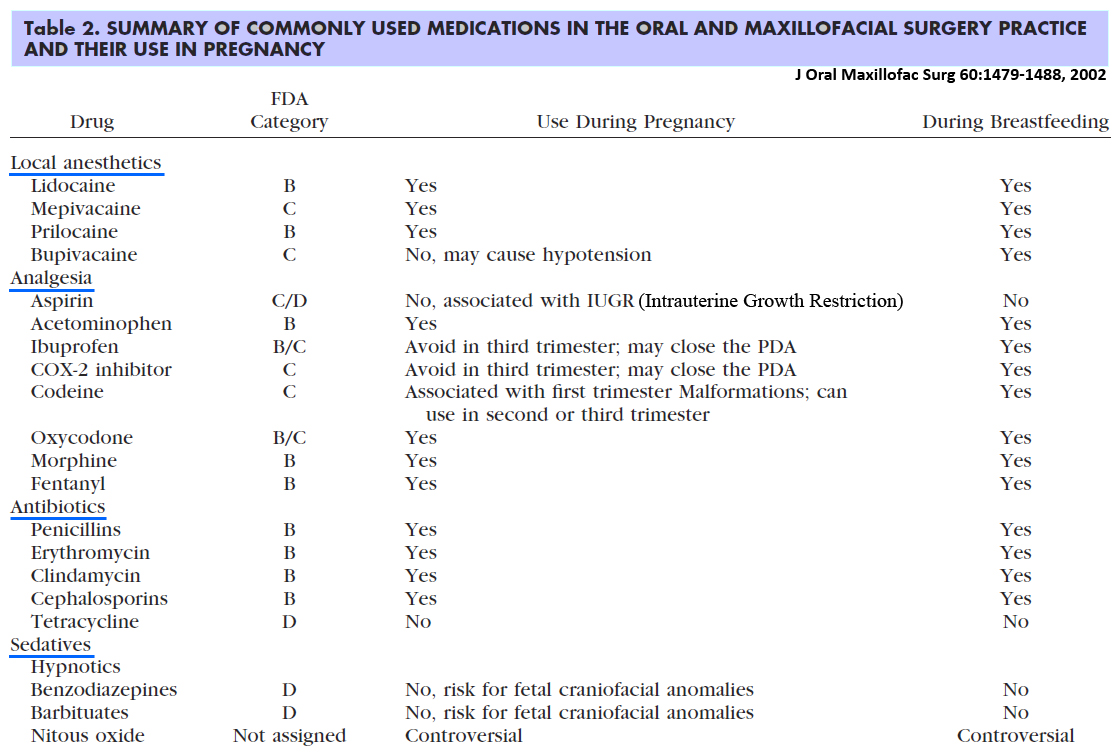
Meds for Pregnant Pts
Disclaimer
This site was created to help guide OMFS interns and residents through their residency. It is created for educational use only. All images belong to the sources below.
1) www.wikipedia.com
2) www.tufts.edu
3) images.google.com
5) Peterson's 2nd Ed.
6) http://www.dentaltraumaguide.org/
7) The Maxillofacial Wilderness Guide – Turner, DDS, MD